
Oral surgery
Nowadays modern surgical techniques in dentistry and materials make it possible to replace both hard and soft dental and periodontal tissues.
In our clinic, the most common surgical procedures are apicotomy or root apex removal, wisdom tooth removal, and periodontal surgery.
Apicotomy
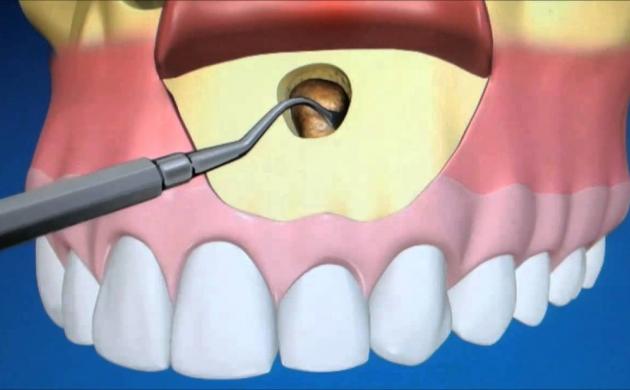
Apicotomy or removal of the root tip (apex) is a surgical procedure in which a part (infected tip) of the tooth root is removed in order to preserve the affected tooth. Additionally the surrounding inflammatory tissue is removed in the procedure, which may also form a cyst.
The bone defect at the site of the removed inflammatory focus and the tip of the root will gradually be filled with new healthy bone by the organism.
The purpose of the apicotomy is to maintain a dead tooth that did not respond appropriately to the endodontic treatment.
The success rate of these interventions is 70-75%, but if we can pre-cure the roots, the success rate is more than 90%.

Removing Wisdom teeth
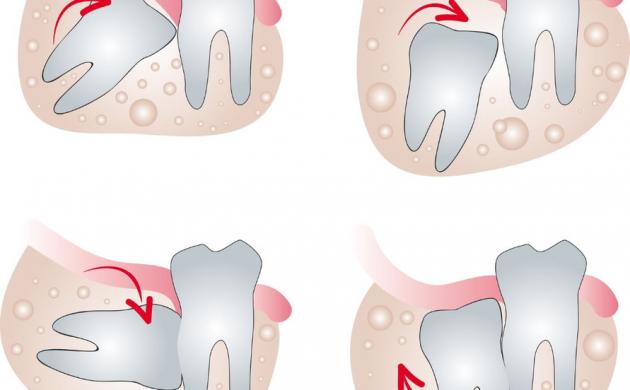
Wisdom teeth often cause problems, such as pain. Often they do not have enough space in the mouth, have an unusual direction of growth or are partially impacted and as such represent the ideal environment for inflammation of periodontal tissue (pericoronitis).
The removal of one or more wisdom teeth is necessary for the following possible reasons:
- inflammation of the soft tissue and / or bone around the tooth (pericoronitis)
- formation of a cyst from a dental follicle - a sac surrounding an impacted tooth
- damage to the adjacent tooth that disrupts the growth of the impacted wisdom tooth
- "inflammation focus" that can be a cause of some systemic diseases or facial pain
- teeth crowding in the dental arch, which can result in the incorrect position of individual tooth and complicates orthodontic treatment
- planned prosthetic treatment
- the non-grown wisdom tooth can resorb the roots of the fully grown second molar.
Periodontal surgery
Periodontal surgery includes:
- soft tissue correction (covering recessions, augmenting soft tissue and correcting gingival margin)
- hard tissue augmentation, including sinus lift
- classic periodontal surgery to treat periodontal disease.
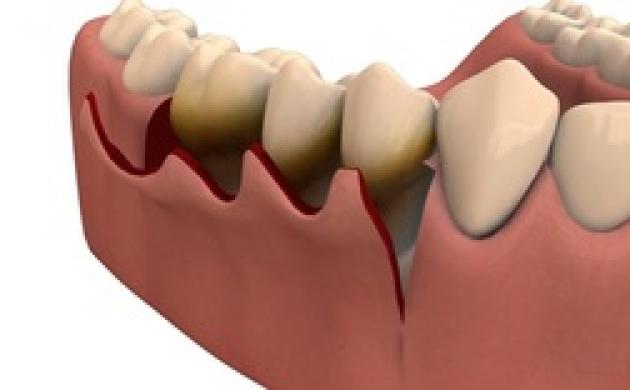
When creating a harmonious and beautiful smile, not only white dental tissues (teeth) are important, but also the aesthetics of the gum. This can be achieved using various (micro) surgery techniques, where defects are filled with soft and / or hard tissues. It is sometimes necessary to remodel existing tissues (eg. surgical lengthening of the clinical crown) to obtain symmetry and aesthetic proportions of the gums.
Surgical procedures that help correct the gums or morphological defects of the soft periodontal tissues and supporting bone tissue are also called mucogingival surgery or plastic surgery in the mouth. The most common surgical procedures are covering of the gum recession with a flap and augmentations (tissue addition).
Bone defect corrections are performed using the techniques of regenerative surgery and the use of transplants.
Advanced periodontal disease or peri-implantitis can lead to major bone loss and the formation of so-called bone craters. These are very difficult to cure with classic periodontal treatment.
With the help of various techniques of regenerative surgery and the use of transplants, the bone defects are corrected to prolong the life of the tooth or implant.
-
Apicotomy
Apicotomy
Apicotomy
Apicotomy or removal of the root tip (apex) is a surgical procedure in which a part (infected tip) of the tooth root is removed in order to preserve the affected tooth. Additionally the surrounding inflammatory tissue is removed in the procedure, which may also form a cyst.
The bone defect at the site of the removed inflammatory focus and the tip of the root will gradually be filled with new healthy bone by the organism.
The purpose of the apicotomy is to maintain a dead tooth that did not respond appropriately to the endodontic treatment.
The success rate of these interventions is 70-75%, but if we can pre-cure the roots, the success rate is more than 90%.


-
Removing Wisdom teeth
Removing Wisdom teeth
Removing Wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth often cause problems, such as pain. Often they do not have enough space in the mouth, have an unusual direction of growth or are partially impacted and as such represent the ideal environment for inflammation of periodontal tissue (pericoronitis).
The removal of one or more wisdom teeth is necessary for the following possible reasons:
- inflammation of the soft tissue and / or bone around the tooth (pericoronitis)
- formation of a cyst from a dental follicle - a sac surrounding an impacted tooth
- damage to the adjacent tooth that disrupts the growth of the impacted wisdom tooth
- "inflammation focus" that can be a cause of some systemic diseases or facial pain
- teeth crowding in the dental arch, which can result in the incorrect position of individual tooth and complicates orthodontic treatment
- planned prosthetic treatment
- the non-grown wisdom tooth can resorb the roots of the fully grown second molar.

-
Periodontal surgery
Periodontal surgery
Periodontal surgery
Periodontal surgery includes:
- soft tissue correction (covering recessions, augmenting soft tissue and correcting gingival margin)
- hard tissue augmentation, including sinus lift
- classic periodontal surgery to treat periodontal disease.
When creating a harmonious and beautiful smile, not only white dental tissues (teeth) are important, but also the aesthetics of the gum. This can be achieved using various (micro) surgery techniques, where defects are filled with soft and / or hard tissues. It is sometimes necessary to remodel existing tissues (eg. surgical lengthening of the clinical crown) to obtain symmetry and aesthetic proportions of the gums.
Surgical procedures that help correct the gums or morphological defects of the soft periodontal tissues and supporting bone tissue are also called mucogingival surgery or plastic surgery in the mouth. The most common surgical procedures are covering of the gum recession with a flap and augmentations (tissue addition).
Bone defect corrections are performed using the techniques of regenerative surgery and the use of transplants.
Advanced periodontal disease or peri-implantitis can lead to major bone loss and the formation of so-called bone craters. These are very difficult to cure with classic periodontal treatment.
With the help of various techniques of regenerative surgery and the use of transplants, the bone defects are corrected to prolong the life of the tooth or implant.

