23.07.2018
Procedure of inserting a dental implant
The implant insertion
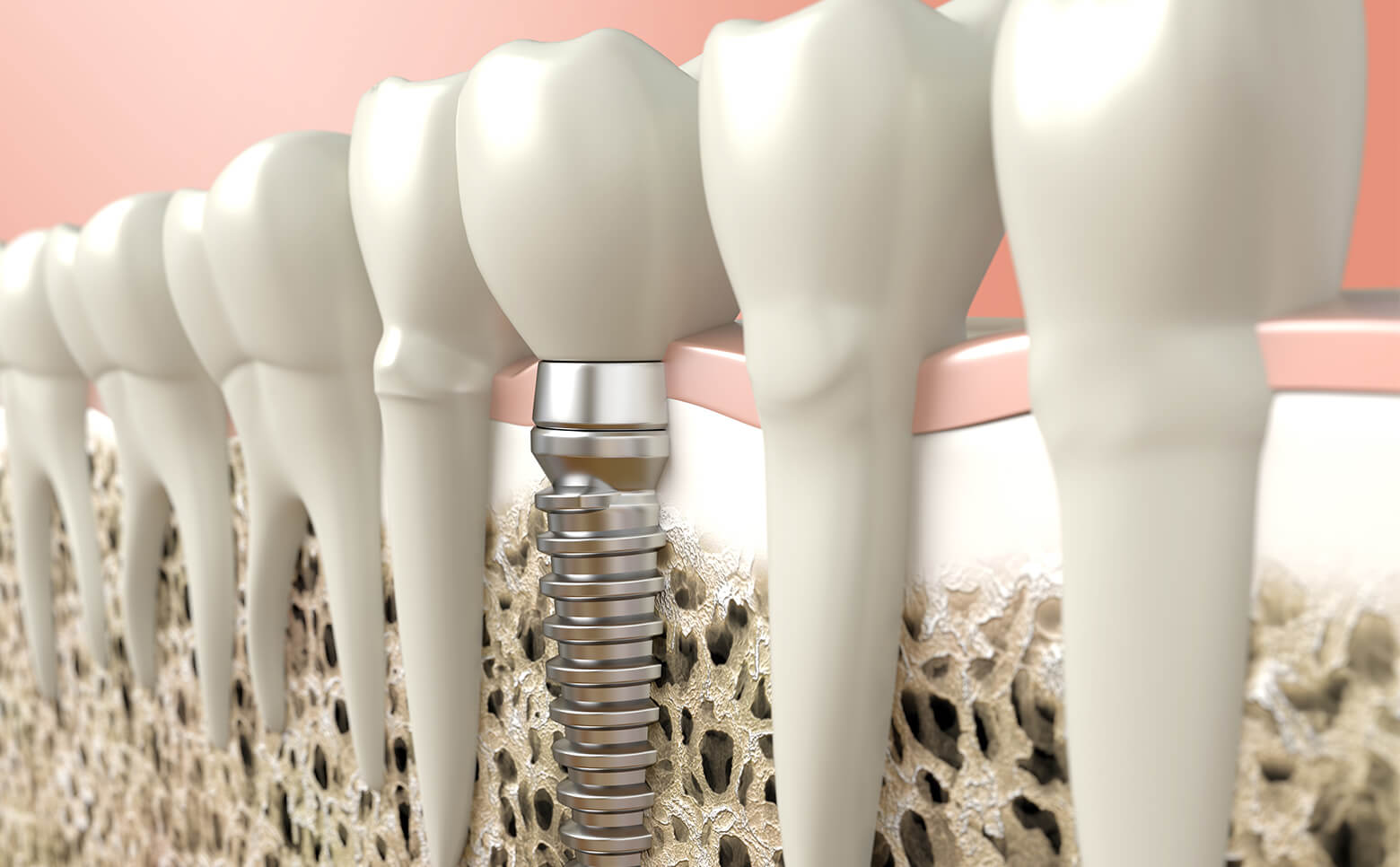
The implant is a dental root-like implant that replaces lost teeth. It is made of biocompatible material; most often it is titanium.

The artificial titanium root is surgically inserted into the bone and fused with it. The procedure is painless as it is performed under local anesthesia. Using a special instrument, prepare a bone bed and insert a dental implant into it. The mucosa or gum is closed again with surgical sutures. After the procedure, moderate and transient swelling of the face or lips is possible, the pain is usually mild after the procedure, and practically none with the help of painkillers. The sutures are removed 10-14 days after surgery.
Implants are provided with prosthetic implants (i.e. crown, bridge, prosthesis) and replaced in the same way as prosthetic dentures, and in most cases the implant itself can remain in the jaw for a life time if the appropriate hygiene and regular maintenance are performed.
What after insertion?
The healing and re-implantation of a dental implant typically takes two to six months. During this time, the implant is not allowed to be loaded or chewed at the insertion site in principle, as its ingroup may endanger it.
After this period, the mucous membrane over the implant is interrupted with a short intervention, and a particle can be screwed into it, which allows the mucosal passage to form and the subsequent connection between the implant and the prosthetic replacement.
After two weeks from the procedure, the dentist can start making a suitable prosthetic replacement. During healing and growing, you can use a temporary prosthetic replacement (bridge, prosthesis), which can be adjusted accordingly.
The healing and implant healing time can be shortened under good bone conditions. In some cases, prosthetic procedures can be resumed as soon as the implant is inserted. In the latter case, the risk of failure may be slightly higher.
Risk factors
The risk factors for implant therapy are small; Dental implants are a safe and reliable way of replacing lost teeth. The ten-year implant survival is as high as 95 %. As with any care, the success of implant therapy is the best in a perfectly healthy organism. Durability of implants can be exacerbated by some spreads and systemic diseases.
Most often factors that can increase the risk of premature dental implant loss are:
- smoking (complete cessation of smoking one week before surgery and eight weeks after surgery reduces the risk of implant loss)
- periodontal disease
- Diabetes
- pre- treatment with biologicals (bisphosphonates - commonly used in the treatment of advanced osteoporosis, prostate cancer ...)
- condition after irradiation and chemotherapy
- bruxism
- taking bisphosphonates (biological drugs).
Periimplantitis and its treatment
As with teeth, inflammation of the tissues can occur at the implant. Due to the shape and structure of the implant, treatment of peri-implantitis is more difficult and less successful than periodontitis. For the more severe forms, surgery is required. The only scientifically proven method of treating periimplantitis that shows slightly better results compared to other surgical procedures (peeling and smoothing the implant surface, the use of various disinfectant coatings, laser treatment) is Perio-flow treatment (EMS). In our office we perform cleaning of implant surfaces with Perio-flow.

Sinus lift
In the upper jaw area of the posterior teeth (molars and premolars), it often happens that there is not enough bone to insert the implants. The sinus lift procedure is used to lift the sinus envelope and insert an artificial bone underneath it to allow the implant to be inserted. When enough bone is available to decide on an internal sinus lift, the procedure is quick, easy, and has similar mild postoperative consequences to implantation itself.

